28+ Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
28+ Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology. Smooth muscle is not under voluntary control; It is divided into two subgroups;
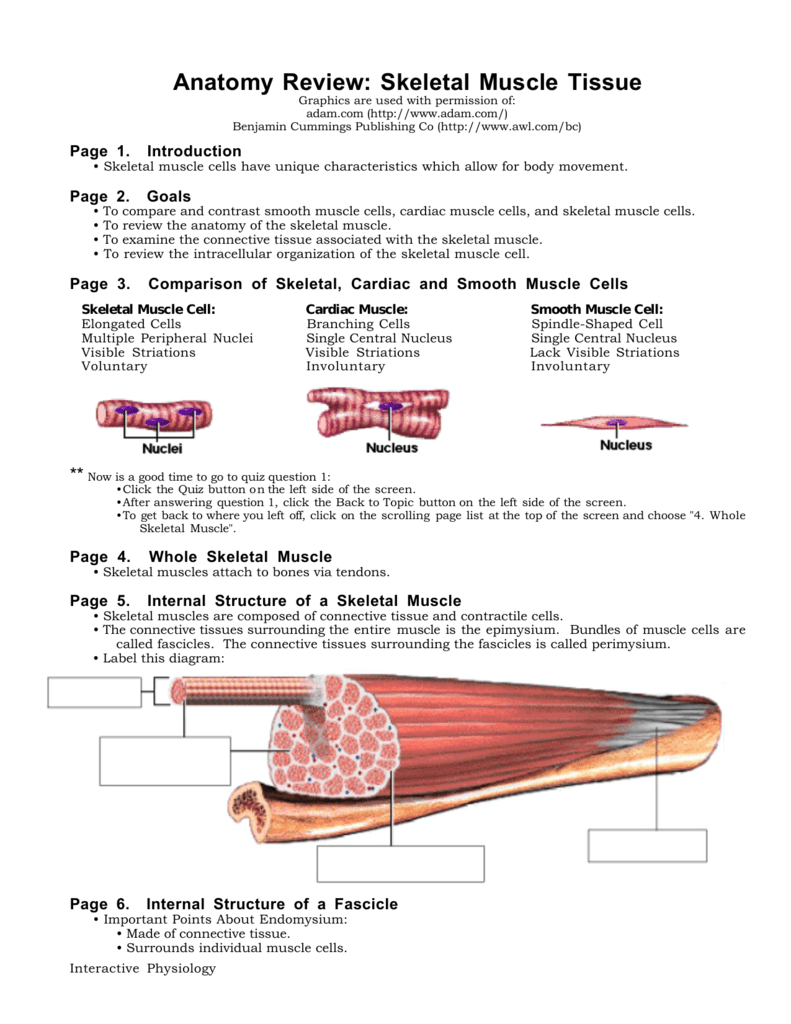
Each muscle type has unique cellular components, physiology, specific functions, and pathology.
A muscle fiber (cell) has special terminology and distinguishing characteristics: The main types of muscle tissue are: Identify skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle cells by anatomical features. Tissue 11.7 cardiac and smooth muscle cardiac and smooth muscle have special structural and physiological properties related to their distinctive functions.
Comments
Post a Comment